The endocannabinoid system is composed of endocannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors, and is involved in the regulation of key physiological and pathological processes. Endocannabinoids are natural, lipid-based signaling molecules that act through two receptors, cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2). The CB1 receptor is primarily found in the brain and spinal cord, and on peripheral organs and tissues; it is the target of the natural endocannabinoid Anandamide. CB1 is also the target of the plant phytocannabinoid THC. A second endocannabinoid, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol targets both CB1 and CB2. Research has shown that the endocannabinoid system serves important protective functions in the body. For example, it stops pain signals before they reach the spinal cord and it boosts the body’s ability to adapt to stressful situations.

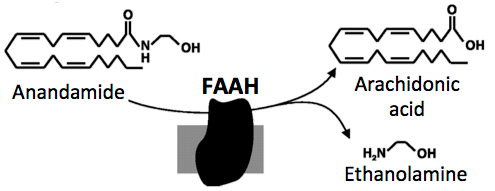
Anandamide is deactivated by the enzyme FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase), which is an attractive pharmaceutical target. Research pioneered by Exxel Pharma’s CSO, Daniele Piomelli, and other academic labs, has shown that FAAH-mediated deactivation of anandamide can be blocked by small molecules. Inhibition of FAAH increases anandamide levels and signaling, thereby boosting the protective effects of the endocannabinoid system.
Exxel Pharma’s URB937 and URB597-based ARNs are examples of small molecule therapeutics that enhance anandamide signaling by blocking FAAH, thereby promoting different therapeutic effects. Some of the clinical applications of FAAH inhibition include chronic cough, pain, addiction, anxiety, PTSD and insomnia.
A list of published URB937 data, including work from international, academic research laboratories, can be found here.
Published URB597 data, including work from international, academic research laboratories, can be found here.
For more information, please contact us.